What is Electrical Insulation?
Definition and Core Principles
Electrical insulation is a material that strongly resists electric current. It does not let electrons move freely through it. This makes it a non-conductor. We measure its strength using “dielectric strength.” This tells us how much voltage the material can handle before breaking down. It’s often shown in volts per mil or kilovolts per millimeter.
Electrical Insulation works by creating a barrier. This barrier keeps electric currents in their proper path. Without it, electricity would go where it shouldn’t. This prevents wires from touching and causing sparks or fires. It keeps energy flowing only where it belongs.
Properties of Insulating Materials
Insulating materials have many important features. These features decide where and how we use them. Choosing the right material is key for safety and performance. Each property plays a role in how well the electrical insulation works.
- Electrical Properties:
- Dielectric strength: The maximum voltage a material can stand before breakdown.
- Volume resistivity: How much a material resists current flowing through its bulk.
- Dielectric constant: How well a material stores electrical energy in an electric field.
- Dissipation factor: How much electrical energy is lost as heat within the insulation.
- Thermal Properties:
- Thermal conductivity: How well heat moves through the material.
- Temperature resistance: The highest temperature a material can handle without harm. This includes its working temperature and its breakdown temperature.
- Mechanical Properties:
- Flexibility: How easily it bends without breaking.
- Tensile strength: How much it can stretch before breaking.
- Abrasion resistance: How well it stands up to rubbing or scraping.
- Chemical resistance: How well it resists damage from chemicals.
- Environmental Properties:
- Moisture resistance: How well it prevents water absorption.
- UV resistance: How well it handles sunlight without degrading.
- Flame retardancy: How well it resists catching fire or spreading flames.
Types of Insulating Materials

Insulating materials come in many forms. They are chosen based on their job. Each type has unique benefits.
Solid Insulators
Solid insulators are common in almost all electrical devices. They are strong and reliable. Their varied forms allow for many uses.
- Plastics and Polymers: Materials like PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) often cover household wires. Polyethylene is great for outdoor cables due to its water resistance. PTFE (Teflon) handles high temperatures and chemicals well. Silicone rubber is flexible and good for high voltage. These materials are lightweight and easy to shape.
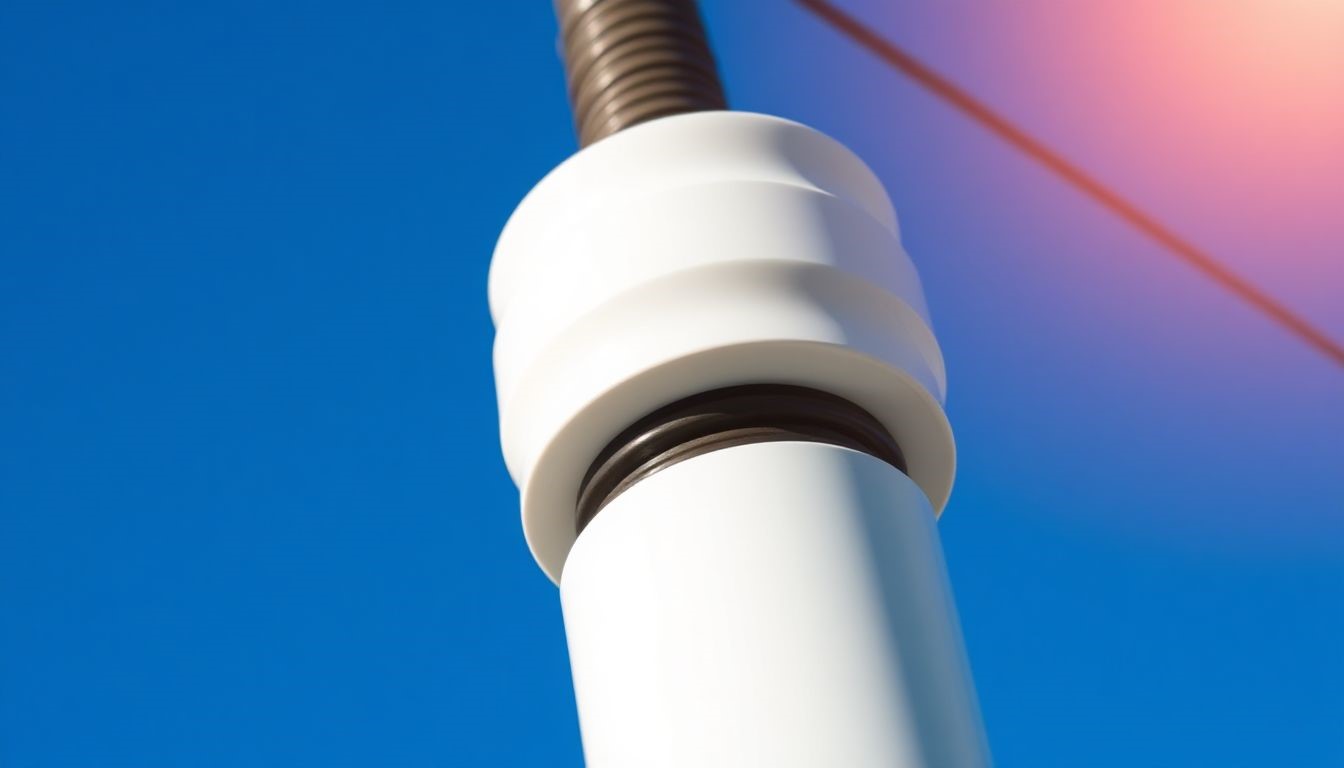
- Ceramics: Porcelain and alumina are excellent for high voltage use. You often see porcelain on power poles. They have very high dielectric strength and can handle extreme heat. Ceramics are rigid and resistant to many elements.
- Composites and Laminates: These combine different materials for better performance. Fiberglass-reinforced epoxies are strong and resist heat and electricity well. Mica-based laminates handle high temperatures and provide great electrical insulation. They offer enhanced mechanical and electrical properties.
Liquid Insulators
Liquid insulators are often found in large electrical equipment. They do more than just insulate. They also help keep things cool. This dual role is crucial for big systems.
- Transformer Oils: Mineral oil is common in power transformers. It acts as an insulator and helps cool the transformer. Synthetic esters are another type, offering better fire resistance and environmental benefits. These oils prevent arcing and help manage heat.
- Silicone Fluids: These liquids are stable across wide temperature ranges. They have good dielectric properties. Silicone fluids are used in some specialized transformers and electrical devices. They are also non-toxic, which is a plus.
Gaseous Insulators
Gaseous insulators are important in high-voltage settings. They fill spaces where other insulators might be too bulky. Their nature allows for unique applications.
- Air: Air is a natural insulator. It’s free and always around us. It insulates many everyday electrical items. For instance, the space between bare wires is often just air. This works well for lower voltages.
- Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6): SF6 gas has much better dielectric strength than air. It’s used in high-voltage switchgear and circuit breakers. SF6 helps prevent electrical breakdown in compact spaces. It’s highly effective for critical power systems.
Role of Electrical Insulation in Safety
Electrical insulation is not just about keeping wires apart. It is a core safety feature. It also boosts how well electrical systems work. Good electrical insulation means fewer dangers and better operation.
Preventing Electrical Hazards
Poor insulation invites danger. It can lead to serious accidents. That’s why quality insulation is a must. It protects us from many electrical threats.
Preventing Short Circuits and Arcing
Electrical Insulation prevents unwanted paths for electricity. It stops current from flowing between conductors that should not touch. A short circuit happens when this fails. This can cause a sudden surge of current. Arcing, a bright electrical discharge, can then occur. This creates intense heat. Proper electrical insulation stops these dangerous events. A frayed electrical cord, for example, can expose bare wires. This could cause a short circuit and quickly start a fire.
Protecting Against Electric Shock
Electrical Insulation puts a vital barrier between you and live wires. It keeps electrical current contained. This protection is key to preventing electric shock. When electrical insulation fails, current can escape. If you touch an uninsulated live wire, current flows through your body. This can cause severe injuries or even death. Each year, thousands of people suffer electric shocks. Many cases are due to poor or damaged insulation. Grounding works with insulation to direct fault currents safely away.
Fire Prevention
Insulating materials often have special properties to fight fire. Flame-retardant electrical insulation slows or stops fire from spreading. This is crucial for building safety. Overheating wires, due to poor insulation or too much current, can also cause fires. The insulation itself might catch fire. This risk is very real. For instance, old, brittle wire insulation in a wall can break down. This might cause wires to overheat and spark, leading to a dangerous building fire.
Enhancing Electrical System Performance
Electrical Insulation does more than protect. It also makes electrical systems run better. It helps ensure signals are clear. It saves energy. It also makes equipment last longer.
Ensuring Signal Integrity
In cables and connectors, insulation is vital for clean signals. It stops electrical signals from mixing or leaking. This prevents signal degradation. High-quality insulation keeps data flowing smoothly. The dielectric constant of insulation affects signal speed. It also impacts how signals match up in a circuit. This matters a lot in sensitive electronics.
Improving Energy Efficiency
Good electrical insulation helps save energy. It cuts down on leakage currents. These are small amounts of electricity that escape from conductors. Even small leaks add up to wasted energy over time. Choosing insulation with a low “dielectric loss” helps. This means less energy turns into unwanted heat. This makes the whole system more efficient.
Extending Equipment Lifespan
Insulation protects electrical parts from outside harm. It guards against moisture, dust, and dirt. These things can damage sensitive components. By keeping parts clean and dry, insulation stops early failure. When insulation stays strong, your equipment runs longer. This saves money on repairs and replacements. It’s like a protective shield for your valuable machines.
9 Factors Affecting Electrical Insulation Performance
Electrical insulation works hard every day. But various things can weaken it. These factors can lead to insulation failure over time. Knowing them helps us prevent problems.
1. Environmental and Operational Stresses
The world around electrical equipment impacts insulation. So does how we use it. These stresses can slowly wear down the protective layers.
2. Temperature Extremes
High temperatures are a big enemy of insulation. Heat makes insulating materials break down faster. This reduces their ability to block electricity. Think of it like a rubber band left in the sun. It becomes brittle. Research shows that every 10-degree Celsius increase can halve the life of some common insulating materials. On the other hand, very low temperatures can also cause problems. Materials can lose their flexibility. They might crack when bent or moved. This creates pathways for electricity to escape.
3. Moisture and Humidity
Water is a conductor of electricity. When insulation absorbs moisture, its insulating power drops fast. Water creates paths for current to flow. High humidity means more moisture in the air. This can lead to surface leakage currents. Moisture can also corrode the metal conductors inside. This damage weakens the electrical connection itself.
4. Chemical Exposure
Chemicals can attack insulation. Oils, solvents, acids, and other chemicals eat away at materials. This can make insulation soft, brittle, or gooey. Once damaged, it can no longer block electricity safely. Always pick insulation materials that resist the specific chemicals found in the work area. For example, if wires are near engine oil, they need oil-resistant insulation.
5. Mechanical Stress
Physical force can easily damage insulation. Bending wires too sharply can crack the insulation. Stretching or pulling them too hard can thin out the protective layer. Rubbing or abrasion wears it down. Even strong compression can harm it. Proper installation and careful handling are key. Always treat insulated cables with care.
6. Electrical Stress and Aging
Electricity itself can harm insulation over time. Constant use and sudden surges can degrade materials. This makes them less effective at their job.
7. Overvoltage and Transient Surges
Sudden, large spikes in voltage are called transient surges. Lightning strikes or switching large loads can cause them. These surges can push past the insulation’s limits. If the voltage is too high, the insulation can break down. This creates a direct path for the surge, which can destroy equipment. Surge protection devices help here. They redirect these spikes away from sensitive insulation.
8. Corona Discharge
Corona discharge is a faint, glowing discharge around high-voltage conductors. It happens when the electric field is very strong. It’s like a tiny electrical leak. Over time, this discharge erodes the insulation. It causes microscopic cracks and pits. These small damages add up, weakening the material. Making surfaces smooth and using proper electrical field grading can help reduce corona discharge.
9. Long-Term Aging (Thermal and Electrical)
Electrical Insulation ages slowly over its life. This is due to constant electrical current and surrounding temperatures. Like anything, materials wear out. This gradual degradation makes them less effective. Industry standards define how long insulating materials are expected to last. This depends on their rated temperature and voltage. Regular exposure to heat and electricity speeds up this aging process.
Summary:
Electrical insulation truly is the unseen guardian of our modern world. It is much more than just a material. It ensures the safety of people and buildings. It keeps our electrical systems running smoothly. It boosts their performance and makes them last longer.
Many factors can challenge insulation. High temperatures, moisture, chemicals, and even the electricity itself can cause problems. That’s why testing and maintenance are so vital. Regular checks and timely repairs keep insulation strong. They prevent dangerous and costly failures.