Principles of Induction Heating
Getting to grips with induction heating means understanding its basic science. This powerful method uses electricity and magnets to make heat. It does this without direct contact with the material being warmed. Let’s break down these core ideas simply.
The Physics of Electromagnetic Induction
Induction heating starts with electromagnetic induction. This idea comes from Faraday’s Law. It states that a changing magnetic field near a conductor creates an electric current in it. Lenz’s Law tells us this current flows to oppose the change. These currents are called eddy currents. They swirl within the metal and are key to how heat forms.
The Role of the Induction Coil
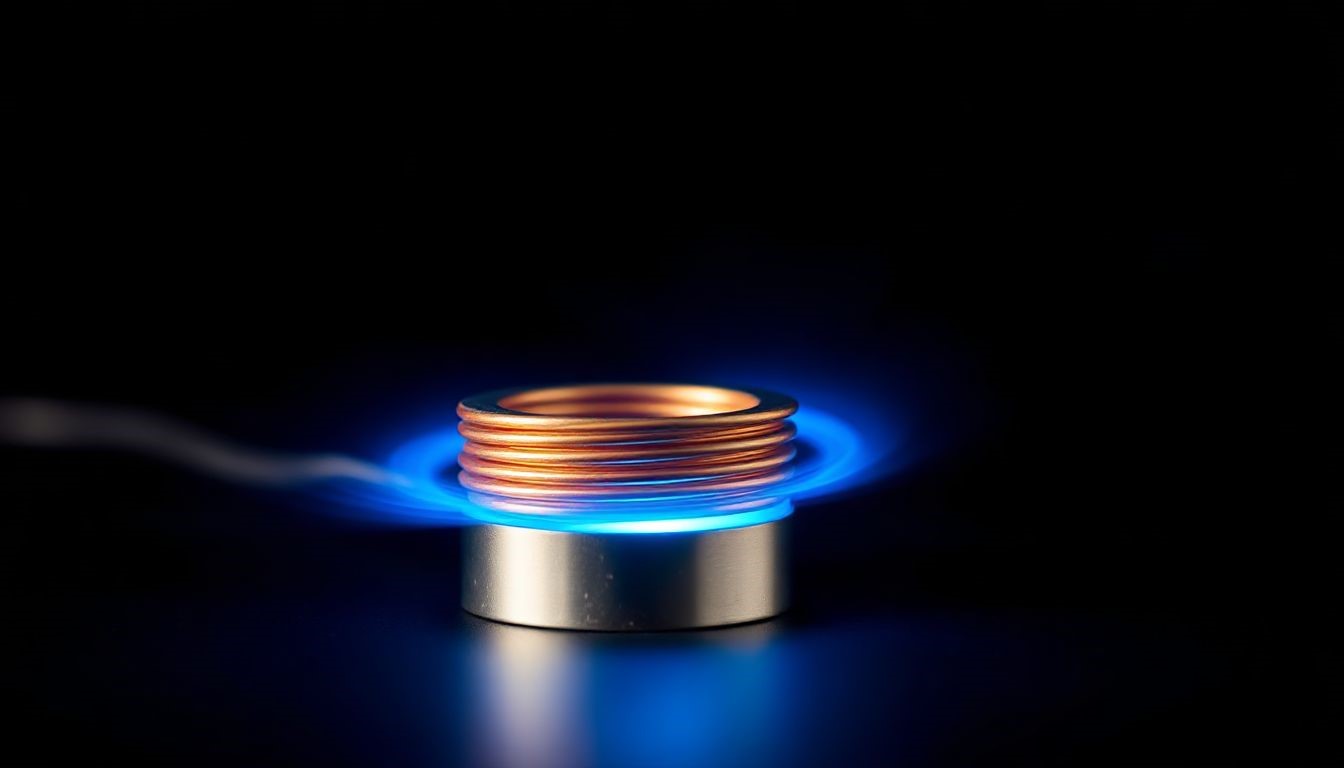
An induction coil is like the engine of the heating system. It’s a wire wound into a specific shape. Electric current flows through this coil, creating a changing magnetic field around it. When a conductive material goes inside or near this field, eddy currents start moving in the material. Coil designs vary greatly, using different shapes and often needing water cooling to keep them from getting too hot themselves.
Heat Generation: Resistive Losses
These induced eddy currents meet resistance as they move through the metal. This resistance causes the material to heat up. It is the same effect as how an electric stove element gets hot, called Joule heating. The ‘skin effect’ means most of this current and heat happen near the surface of the material. This lets us control how deep the heating goes.
Advantages of Induction Heating
Induction heating stands out for many reasons. It offers big benefits over older ways of warming things up. These advantages make it a top choice for modern factories.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
Induction heating sends almost all its energy straight to the part you want to heat. This means very little energy gets lost to the air. Companies save a lot on power bills. Many metal shops report a big drop in energy use after switching from flame heating or ovens. This smart use of power helps both their budget and the planet.
Precise and Rapid Heating
This method lets you reach high temperatures incredibly fast. You can pinpoint exactly where and how much heat you need. This quickness boosts how many parts you can make in an hour. Plus, you get the exact same result every time. For best results, think about how quickly you need things warmed and how even the heat must be when picking a system.
Superior Process Control and Consistency
Induction systems give you amazing control over the heating process. You can set the exact temperature, how long it heats, and the power level. This means every single part gets the same treatment. This leads to products that are always high quality and reduces wasted materials. Automated systems make this consistency even easier.
Environmental and Safety Benefits
One big plus is safety. There are no open flames or hot gases to worry about. This makes the workspace much safer for people. It also cuts down on harmful fumes and pollution. Traditional heating methods often pose more risks and create more emissions. Induction heating helps factories be greener and safer places.
Applications
Induction heating is a workhorse, used in countless ways across many different businesses. Its flexibility allows it to adapt to many tasks. Here are some real-world examples of where it shines.
Metalworking and Manufacturing
In metal shops, induction does a lot. It hardens parts to make them stronger, tempers them for toughness, and anneals them to remove stress. It also brazes and solders parts together with strong, clean joints. Even big jobs like forging metal into shape use induction heat. For example, car makers use induction to harden the camshafts in engines. This makes the parts last longer and work better.
Semiconductor and Electronics Industry
Making electronics needs pure materials and very precise work. Induction heating helps grow perfect crystals, like silicon for computer chips. It also melts and refines special metals used in tiny electronic parts. This ensures the metals are super clean and free of flaws. It is key for creating the high-purity metals found in advanced electronic devices.
Food Processing and Packaging
You might not think of food with induction, but it plays a role there too. It helps sterilize food products, making them safe to eat for longer. It also pasteurizes liquids, like milk, very efficiently. A common use is sealing bottle caps and jars. This makes a strong, tamper-evident seal that keeps food fresh and safe from being opened before you buy it.
Laboratory and Research
Scientists and researchers use induction heating for many tasks. It helps them melt small samples of material quickly. They also use it for preparing samples for testing. Many labs need very specific heating for their experiments. Induction gives them the control they need for these special jobs.
Conclusion
Induction heating stands as a top choice for modern industries. Its benefits in energy use, speed, and exact control are clear. From making car parts strong to sealing food safely, its uses are broad. This method has changed how many tasks are done.
It has truly transformed how factories work. It boosts how much they make, makes products better, and helps the environment. It does all this by cutting energy waste and pollution. This technology truly offers a better way to heat things.
As we look ahead, induction heating will keep growing. Expect more new ideas and ways to use it. It remains a key part of making industrial work smarter, faster, and much cleaner for years to come.