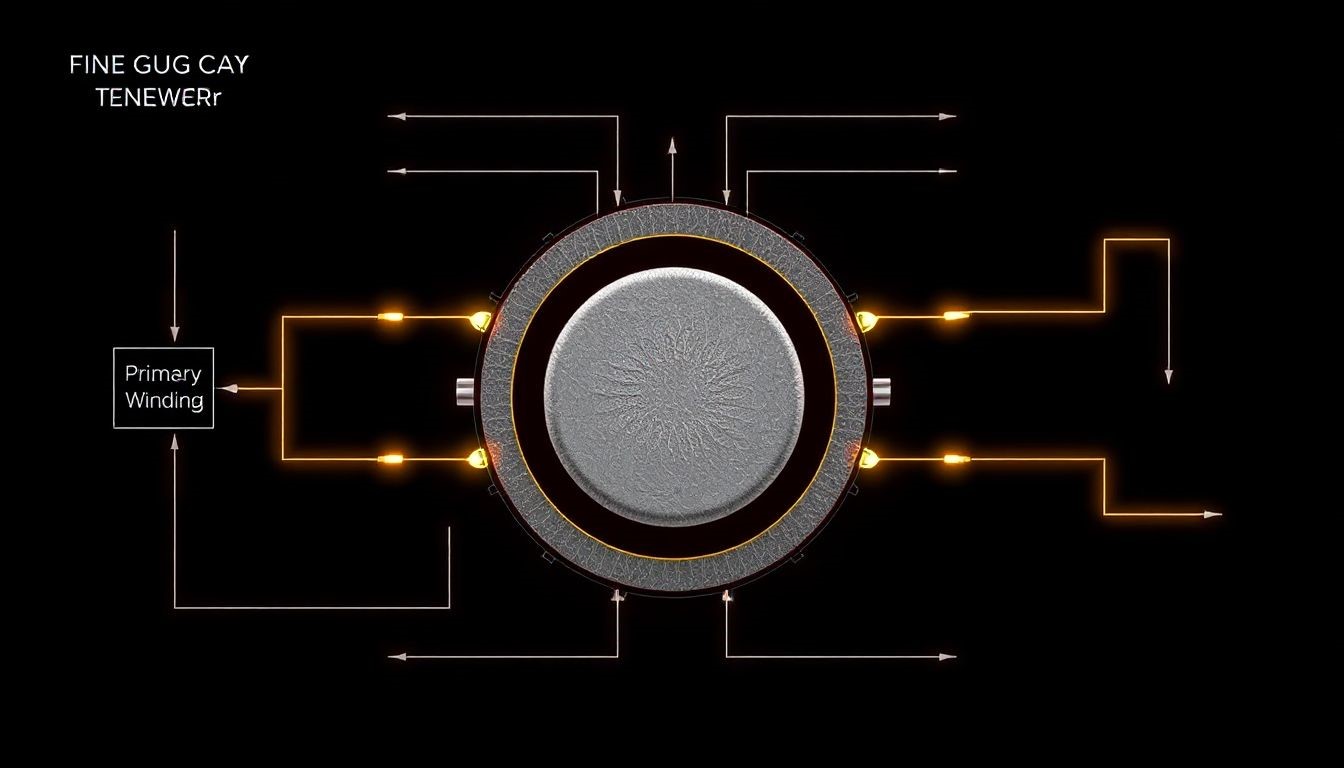
One Line Diagram Electrical
Symbolism in One Line Diagram Electrical Understanding Schematic Representation Old electrical drawings can look like a spider web. Full schematics show every wire and switch in detail. But a one line diagram electrical skips that clutter. It uses one line for each circuit path. This makes it easier to spot issues or plan changes. Engineers … Read more